Curing induced distortion in adhesive bonding of dissimilar materials
Background
- To reduce vehicle structure weight, lightweight materials (aluminum, composite, high strength steel) are used in autobody manufacturing, which pose a challenge for joining.
- Adhesive bonding offers advantages for joining similar and dissimilar materials.
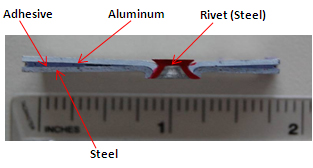
- Severe curing induced distortion is observed for aluminum roof-to-steel body side assembly in Fuel Efficiency Learning Vehicle (FELV).
- Little information is available concerning curing induced distortion using crash-toughened adhesive. Tool or methodology is needed for body design to minimize bonding induced distortion.
Objective
- Develop predictive capability to analyze dimensional variation of adhesive bonded joint
- Establish design and manufacturing guidelines for adhesive bonding of body structures
Approach
- Modeling of rivet-bond joint
- Modeling adhesive cure processes, including heating, curing and cooling
- Coupon-level modeling and experimental verification of dissimilar materials
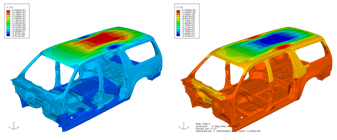
- Structural modeling: aluminum roof-to-steel body assembly of FELV and NG_Delta
- Methods to reduce curing-induced distortion
Researchers
- Liang Zhou
- Baiyan (Brian) He